Signal Processing¶
Simplifying a Signal¶
Whenever you seek to apply a tool on your data that will operate on each value and this tool is time and / or resource consuming, it might be a good idea to operate on as few values as possible. Simply removing duplicated values is not always the best approach. Think of a discharge time series where you want to calculate an index that depends on a previous state.
Set up a test case¶
The example below will show the idea behind the
simplify method of the signal submodule. At
first some imports.
In [1]: import numpy as np
In [2]: import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
In [3]: import matplotlib as mpl
In [4]: mpl.style.use('ggplot')
And now setup and plot the test signal.
In [5]: x = np.array([1., 1.2, 1.5, 1.5, 1.5, 1.5, 1.6, 1.5, 1.6, 1.5, 1., 0.5,
...: 0.2, 0.3, 0.2, 0.3, 0.2, 0.3, 0.2, 0.3, 0.2, 0.3, 0.2, 0.3,
...: 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.7, 1., 1.5, 1.6,
...: 1.5, 1.6, 1.5, 1.6, 1.5, 1.6])
...:
In [6]: plt.plot(x, '.--r');
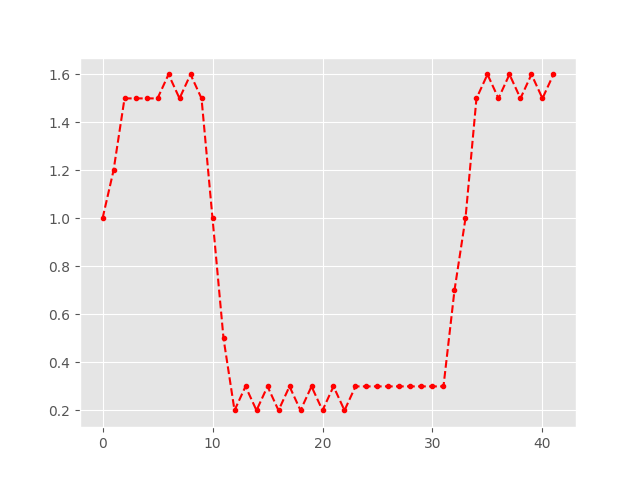
Handling replicas¶
There are a number of replications. We want to get rid of those.
In [7]: from hydrobox.toolbox import simplify
In [8]: plt.plot(simplify(x, flatten=False), '.--r');
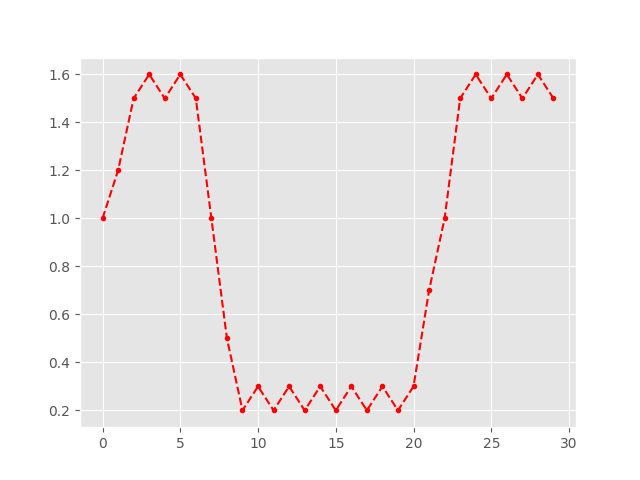
- Look at the amount of markers in both plots, where the signal gave a constant
- value. The replicas got dropped from the signal.
Handling sensor precision noise¶
So far, this only removed subsequent value duplicates. The other signal
information this method can simplify is the constant repetition of two values.
This usually happens in environmental sensors either in constant conditions
or during really slow state changes. In these cases the signal can alternate
between two states within the sensor resolution. These recordings can be evened
out by setting the flatten attribute to True.
In [9]: plt.plot(simplify(x, flatten=True), '.--r');
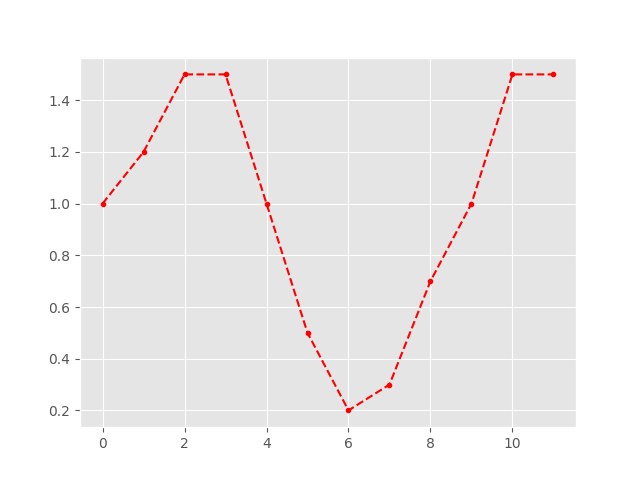
Of course, the index information was completely lost. In this example the x-axis is just counting the occurrences of values. In case you need the index information for further analysis, you have to extract the index and preserve it, before calling the simplify method.
Important
The preservation of indices, whenever the data is of type pandas.Series
is planned for a future release.
Warning
Keep in mind that two very strong assumptions are underlying this method. It does change the signal dramatically. Ensuring that the sensor noise assumption is correct is completely up to you.